When starting a new project in AutoCAD, the first step is often overlooked yet absolutely essential—setting up units, options, and templates correctly. Without these basics, even the most skilled drafting can end up inaccurate or inconsistent. Whether you’re an engineering student, architect, or professional designer, understanding these fundamentals ensures your drawings are precise, efficient, and ready for collaboration.
This guide walks you through everything you need to know:
- How to set and manage units in AutoCAD (metric & imperial)
- Customizing AutoCAD options for better workflow
- Working with metric and imperial drawings step by step
- Using templates to save time and maintain standards
Must Read 🧊 Understanding the AutoCAD Interface – A Complete Overview of Its Important Features
1. Setting Units in AutoCAD
Why Units Matter
Units are the foundation of any technical drawing. Defining them correctly at the start prevents scale mismatches, calculation errors, and confusion later in the project.
How to Set Units
- Type
UNITSin the command line and press Enter. - The Drawing Units dialog box opens.
- Choose your preferred unit type:
- Architectural – feet and inches (common in building drawings in the U.S.)
- Decimal – general decimal values (widely used in engineering fields)
- Engineering – feet and decimal inches
- Fractional – inches expressed in fractions
- Scientific – exponential notation (useful for very large or very small measurements)
Adjusting Precision
- Lengths and angles can be set up to eight decimal places.
- Higher precision is ideal for technical or scientific applications, while lower precision is enough for conceptual sketches.
Displaying Coordinates
- Enable coordinate display on the status bar.
- This helps when drafting with exact coordinates—a common requirement in surveying and civil engineering projects.

Must Read 🧊 Top AutoCAD 2D Commands Every Beginner Should Learn
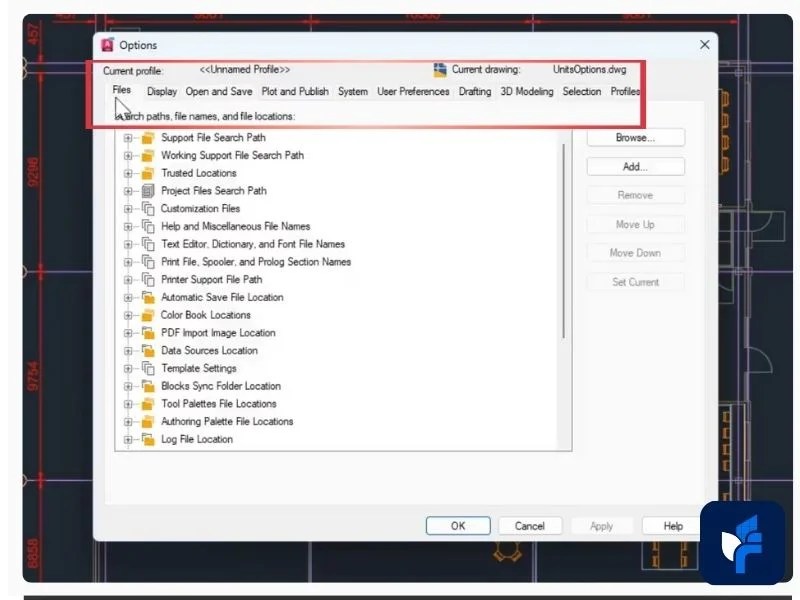
2. Setting AutoCAD Options
AutoCAD’s Options dialog box allows you to customize your workspace so it fits the way you work best.
Accessing the Options Box
- Right-click in an empty area of the drawing space.
- Select Options from the menu.
Key Tabs to Know
- Files Tab
- Controls file paths such as autosave and template locations.
- For safety, set autosave files to a cloud drive or network folder—so you never lose data during a system crash.
- Display Tab
- Lets you personalize the appearance of your workspace.
- Example: switch your model space background to white for easier plotting.
- User Preferences Tab
- Manages insertion scale when working with drawings created in different units.
- Ensures millimeter-based and inch-based drawings scale correctly when inserted into the same project.
Customizing these options improves efficiency, consistency, and collaboration across teams.
Must Read 🧊 How to Install and Set Up AutoCAD 2D/3D
3. Working with Drawings in Metric Units
In most countries, especially outside the U.S., metric units are the standard for engineering and construction drawings.
Setting Up Metric Units
- Open the drawing file units-METRIC.dwg (or start a new one).
- Check the coordinate readout on the status bar—it should display values in millimeters.
Drawing Example
- Activate the Line command.
- With Dynamic Input enabled, specify distances directly.
- Example: draw a line 2500 mm horizontally, then another 1250 mm vertically.
Accuracy Tools
- Polar Tracking – keeps your lines aligned at fixed angles (like 90°).
- Object Snap Tracking (OSNAP) – ensures points snap to exact endpoints, midpoints, or intersections.
These tools help maintain precision in large-scale engineering projects.

Must Read 🧊 How can customizing toolbars improve my workflow in AutoCAD
4. Working with Drawings in Imperial Units
In the U.S., construction and architectural drawings usually rely on imperial units (feet and inches).
Setting Up Imperial Units
- Open the file Units-IMPERIAL.dwg.
- Use the UNITS command to confirm settings:
- Type: Architectural
- Precision: 1/16 inch
Drawing Example
- Use the Line command.
- Input distances in the format feet’ inches”.
- Example: to draw 8 feet 6 inches, type
8'6".
- Example: to draw 8 feet 6 inches, type
Features That Help
- Dynamic Input – shows distance and angle while you draft.
- Polar Tracking – ensures perfect vertical or horizontal lines.
- Object Snap Tracking – locks points at precise intersections or midpoints.
Pro Tip
Master a few shortcuts—like L for Line, C for Circle, and REC for Rectangle—to draft much faster.
Must Read 🧊 Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Editing Command in AutoCAD
5. Using AutoCAD Templates
Templates are a major time-saver in AutoCAD. They help you maintain consistency across different projects.
Why Templates Are Useful
- Predefined units (metric or imperial)
- Standard layers, line types, and text styles
- Built-in title blocks and borders
- Saved dimension and annotation styles
Creating a Template
- Set up a drawing with all your preferred settings.
- Save the file as a .DWT (Drawing Template).
- Use it whenever you start a new project—no need to repeat setup steps.
Templates are especially valuable for teams, as they ensure that everyone follows the same drawing standards.
Getting comfortable with units, options, and templates in AutoCAD is more than just a beginner’s task—it’s the foundation of professional drafting. Whether you’re working in millimeters for international projects or feet and inches for U.S. construction, setting up your workspace properly saves time, reduces errors, and ensures your drawings are consistent and accurate.
Once you’ve mastered these basics, you’ll find it much easier to move on to advanced AutoCAD tools and techniques, knowing that your foundation is solid.
FAQ’s
Q1. How do I set units in AutoCAD?
Type UNITS in the command line, then select the unit type (architectural, decimal, engineering, etc.) and precision level from the dialog box.
Q2. What is the difference between metric and imperial units in AutoCAD?
Metric units use millimeters or meters, while imperial units use feet and inches. The choice depends on project requirements or regional standards.
Q3. Why are AutoCAD templates important?
Templates save predefined settings like units, layers, and title blocks, ensuring consistency and saving time across multiple projects.
Q4. How can I change AutoCAD background color?
Go to Options > Display Tab and change the model space background color to suit your preference.
Q5. What is the use of polar tracking in AutoCAD?
Polar tracking locks drawing lines at specific angles (e.g., 0°, 90°), helping maintain alignment and precision.





