Walk through any urban skyline today, and you’ll see gleaming facades of glass and metal defining the architectural identity of our era. These aren’t just decorative exteriors—they are curtain walls, a crucial element in modern high-rise construction. Known for their non-load-bearing nature, curtain walls provide both visual appeal and building performance without supporting floor or roof loads. They are engineered to resist environmental forces while delivering aesthetics, daylighting, and energy efficiency.
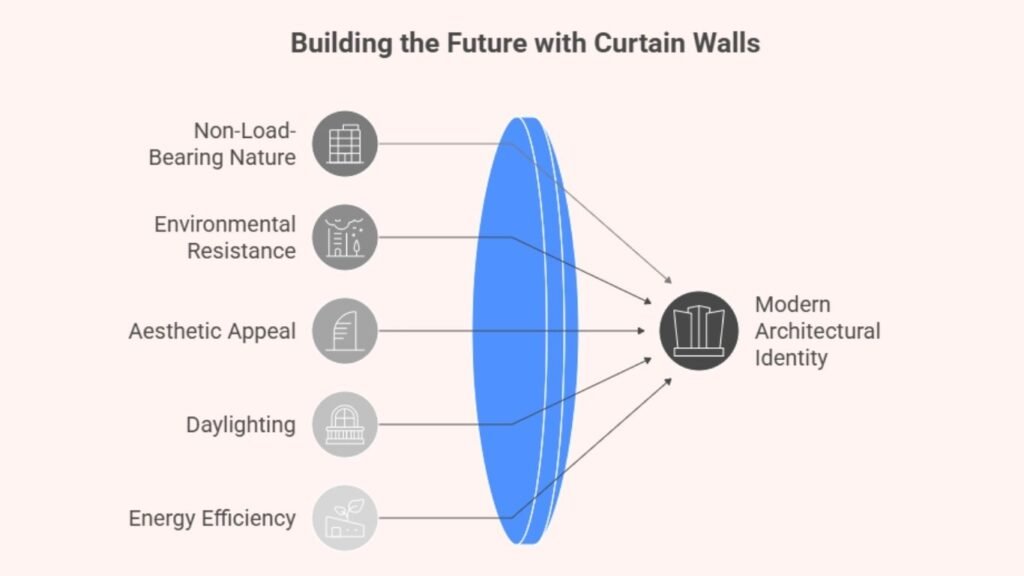
What Is a Curtain Wall System?
A curtain wall system is an external cladding system that is suspended from the main structural frame of a building. Unlike traditional walls that bear the weight of floors or roofs, curtain walls are designed solely to handle their own weight and withstand wind pressure, thermal expansion, seismic activity, and air and water infiltration. Typically made of aluminum frames with glass, metal panels, or stone infill, these systems allow architects to design expansive, light-filled facades that transform the look and performance of a structure.
Key Features and Components of Curtain Walls

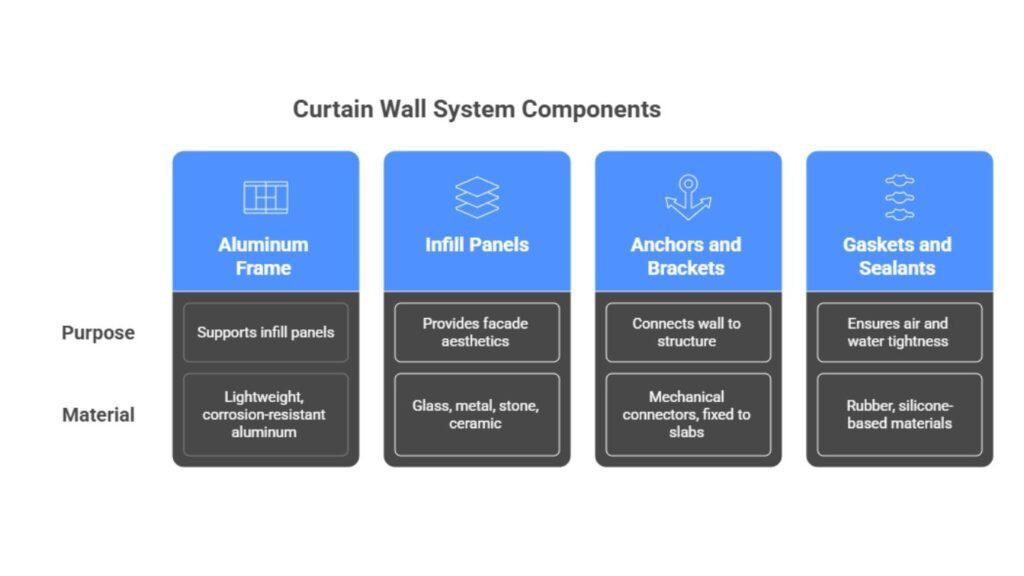
1. Aluminum Frame
- Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and strong
- Supports infill panels and transfers wind load to the structure
2. Infill Panels
- Glass: Clear, tinted, laminated, or double-glazed for insulation
- Metal Panels: Often aluminum composite panels for thermal and fire resistance
- Stone or Ceramic: For aesthetics and unique façade treatments
3. Anchors and Brackets
- Mechanical connectors fixed to slabs or beams
- Engineered to absorb structural movement, wind loads, and seismic activity
4. Gaskets and Sealants
- Essential for air and water tightness
- Typically made of silicone, EPDM rubber, or other elastomers
Types of Curtain Wall Systems
Stick System Curtain Wall
This is the most traditional method where each component—vertical mullions, horizontal rails, infill panels—is assembled on-site. It offers high flexibility in design and is well-suited for projects with complex geometries or limited factory access.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective for small-scale projects
- Customizable on-site
Drawbacks:
- Labor-intensive and time-consuming
- Greater dependency on weather and site conditions
Unitized Curtain Wall System
In this prefabricated system, large curtain wall units are manufactured in factories under controlled environments and installed on-site using cranes. Unitized systems are ideal for high-rise buildings where speed and quality control are essential.
Advantages:
- Faster installation
- Improved quality assurance
- Less site disruption
Drawbacks:
- Higher initial cost
- Limited on-site design adjustments
Performance Benefits of Curtain Wall Systems
Weather Resistance
Curtain walls are rigorously tested for air and water infiltration, ensuring a dry and stable interior environment. Properly sealed joints and drainage paths prevent leaks and water damage.
Energy Efficiency
- Insulated Glazing Units (IGUs): Trap air or inert gas to reduce heat transfer
- Low-E Glass Coatings: Reflect infrared radiation
- Thermal Breaks in Frames: Reduce thermal bridging and enhance insulation
Daylighting and Aesthetics
Curtain walls maximize the entry of natural light, reducing reliance on artificial lighting and improving indoor comfort. Their sleek and modern appearance contributes to a building’s identity and urban presence.
Fire and Acoustic Safety
- Fire-stopping materials between floors limit the spread of smoke and flames
- Laminated or acoustic glass panels reduce external noise, crucial for urban settings
Installation Process
- Design and Engineering: Includes structural analysis, thermal modeling, and coordination with other building systems
- Fabrication: Off-site manufacturing of frames, brackets, and panels to improve precision
- Transportation and Site Prep: Delivery and site logistics planning
- On-Site Installation: Stick or unitized systems installed using scaffolding or cranes
- Glazing and Sealing: Ensures airtightness, weatherproofing, and energy performance
Maintenance and Longevity
Routine maintenance ensures curtain wall systems maintain their appearance and performance over decades. Regular inspection of seals, anchors, and panels is crucial to prevent long-term damage.
- Glass Cleaning: Required to preserve visibility and reflectivity
- Sealant Checks: Prevent air and water infiltration
- Anchor Inspection: Ensure safety and structural integrity
With proper care, curtain walls can perform effectively for 40–50 years or more.
Real-World Applications and Examples
Curtain walls are not limited to skyscrapers—they’re also found in airports, stadiums, hospitals, educational campuses, and commercial complexes. Notable examples include:
- Burj Khalifa, Dubai – Stick system with high-performance glazing
- The Shard, London – Iconic unitized glass façade
- Apple Stores – Structural glass curtain walls for minimalist design
Common Misconceptions
- “Curtain walls are fragile.” Modern systems are engineered to withstand hurricanes, seismic forces, and thermal stresses.
- “They waste energy due to glass.” Advanced glazing and design drastically improve energy performance.
- “Only for high-rises.” Used in mid-rise and even low-rise commercial buildings.
Sustainability and Green Building Certifications
Curtain walls contribute to sustainable architecture by:
- Allowing daylight harvesting
- Reducing energy consumption
- Using recyclable materials like aluminum and glass
- Supporting LEED, BREEAM, and GRIHA certification requirements
Curtain walls represent the intersection of engineering innovation and architectural vision. They define skylines, improve building performance, and shape how occupants interact with natural light and urban views. For developers, architects, and engineers, understanding curtain wall systems is essential to creating structures that are not just functional but truly future-ready.
Explore Civil Engineering Tools
Quick access to essential tools, formulas, and code references—all in one place.





You actually make it seem really easy together with your
presentation but I in finding this matter to be really one thing which I
think I’d by no means understand. It seems too complicated and very vast for me.
I am taking a look forward to your next submit, I will try to get the hang of it!
Thank you so much for your kind words! I’m really glad to hear that the presentation helped make the topic easier to follow. I completely understand that some concepts can feel overwhelming at first—you’re definitely not alone. I’ll keep breaking things down in a clear, step-by-step way in future posts. Feel free to ask any questions anytime—we’re here to help you build confidence as you go. Stay tuned!